
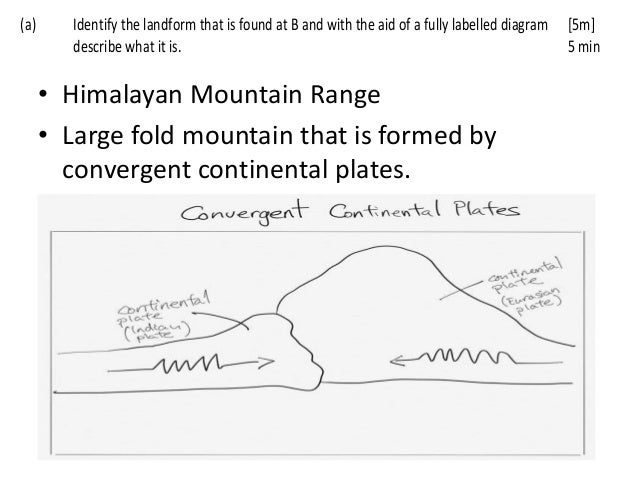
This resulted in a better fit than previous efforts that traced the existing coastlines.

He used true edges of the continents, based on the shapes of the continental shelves. What Wegener did differently was synthesize a large amount of data in one place. These show the true shapes of the continents. Note the light blue, which are continental shelves flooded by shallow ocean water. Antonio Snider-Pellegrini did preliminary work on continental separation and matching fossils in 1858. People noticed the similarities in the coastlines of South America and Africa on the first world maps, and some suggested the continents had been ripped apart. Wegener’s first piece of evidence was that the coastlines of some continents fit together like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. 2.1.1 Early Evidence for Continental Drift Hypothesis Snider-Pellegrini’s map showing the continental fit and separation, 1858. While he did not have the precise mechanism worked out, his hypothesis was backed up by a long list of evidence. After reviewing the scientific literature, he published a hypothesis stating the continents were originally connected, and then drifted apart. His knack for questioning accepted ideas started in 1910 when he disagreed with the explanation that the Bering Land Bridge was formed by isostasy, and that similar land bridges once connected the continents. 1924-1930.Alfred Wegener (1880-1930) was a German scientist who specialized in meteorology and climatology. 2.1 Alfred Wegener’s Continental Drift Hypothesis Because it is so important in understanding how the world works, plate tectonics is the first topic of discussion in this textbook. Many earth processes make more sense when viewed through the lens of plate tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics attributes the movement of massive sections of the Earth’s outer layers with creating earthquakes, mountains, and volcanoes. The concept of plate tectonics was just as revolutionary for geology. Albert Einstein’s relativity and quantum mechanics concepts in the early twentieth century did the same for Newtonian physics.
Charles Darwin’s book on evolution, On the Origin of Species, published in 1859 Gregor Mendel’s discovery of the genetic principles of inheritance in 1866 and James Watson, Francis Crick, and Rosalind Franklin’s model for the structure of DNA in 1953 did that for biology. Several of these idea revolutions forced scientists to re-examine their entire field, triggering a paradigm shift that shook up their conventionally held knowledge. Explain how the tracks of hotspots, places that have continually rising magma, is used to calculate plate motionĭetailed map of all known plates, their boundaries, and movements.Revolution is a word usually reserved for significant political or social changes.Describe the Wilson Cycle, beginning with continental rifting, ocean basin creation, plate subduction, and ending with ocean basin closure.Explain transform boundaries as places where adjacent plates shear past each other.Identify divergent boundaries, including rifts and mid-ocean ridges, as places where plates separate.Identify convergent boundaries, including subduction and collisions, as places where plates come together.Explain how movement at the three types of plate boundaries causes earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building.Describe the physical and chemical layers of the Earth and how they affect plate movement.Describe how the ideas behind plate tectonics started with Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis of continental drift.2 Plate TectonicsĪt the end of this chapter, students should be able to: A layer of shallow ocean limestone (white) has been brought to the top of a mountain by the convergent forces of the Sevier Orogeny.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
